【人気ダウンロード!】 sinus rhythm with pac ecg strip 560990-What is sinus rhythm with pac
• Interpret a rhythm strip and identify life threatening dysrhythmias • Anticipate common dysrhythmia treatment plans • Identify presence of a pacemaker and its proper operation • Apply skills toward the introduction of 12lead EKG analysis Cardiac Anatomy & Physiology Cardiac Anatomy & Physiology Einthoven's Triangle Precordial Leads ECG monitor lead placementGiven a rhythm strip, identify Sinus, Atrial, Junctional and Ventricular dysrhythmias, and Atrioventricular Blocks 4 Identify the appropriate nursing and medical interventions, and first line medications for ECG rhythms 5 Score at least 85% competency on the posttest 4 GLOSSARY Aberrant Conduction Term applied to abnormal (slowed) intraventricular conduction ofBasic EKG Test (100 strips) 01 Identify the following rhythm a Sinus bradycardia b Accelerated junctional rhythm c Sinus rhythm with 1st degree block d

Premature Atrial Contraction Electrocardiogram Wikidoc
What is sinus rhythm with pac
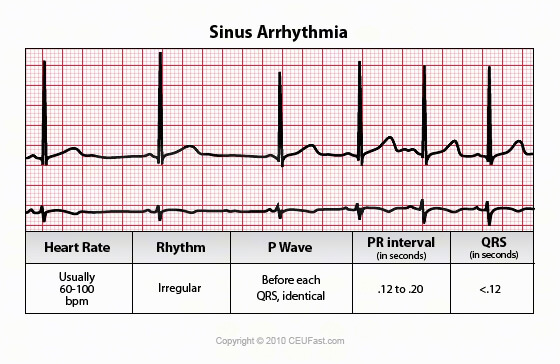
What is sinus rhythm with pac-0807 · An EKG strip with sinus bradycardia would show a regular heart rhythm, with consistent distances between both R waves and P waves P waves will be upright with a smooth and consistent appearance PR intervals will be of normal duration, the QRS complexes will be narrow, and there will be only one P wave for each QRS complexSinus arrhythmia is a normal physiological phenomenon and it is considered a variation of normal sinus rhythm It is defined as an irregularity in the rate of normal sinus rhythm Its main characteristic on the EKG is a variation in the PP intervals greater than 012 s with a normal P wave morphology 1 2



1
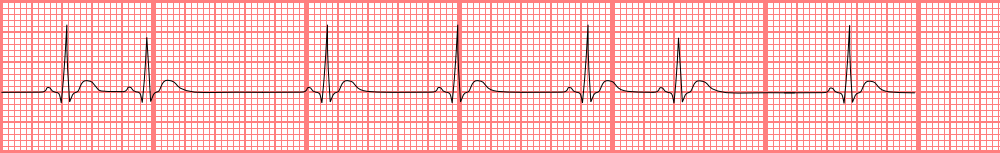
Normal sinus rhythm is the default cardiac rhythm that represents the normal electrical activity through the heart Electrical impulses start at the sinoatrA normal sinus rhythm refers to both a normal heart rate and rhythm Normal heart rates are from 60 to 100 beats per minute The shape of the electrocardiogram (EKG) tracing will exhibit certain key attributes to be considered normal, as discussed below With normal sinus rhythms, the heart beat's electrical impulse originates in the sinoatrial19 Sinus Rhythm with a PAC 4th beat is early and narrow with compensatory pause Atrial Fibrillation (rate 100) Irregular without discernible P waves 21 Sinus Arrhythmia (rhythm
Basic ECG Interpretation Practice Test DIRECTIONS The following test consists of questions • At any time during the test, you can go back to a previous question and edit/change your answer • Please answer each question to the best of your ability, using no external references 1 A Normal Sinus Rhythm B Sinus Tachycardia C NSR with PAC'c D NSR with 1st Degree AV Block E NSR0707 · With this strip, we're going to talk about premature atrial complexes or PACs So you can see that on the righthand side of the strip, it looks really normal It's normal sinus rhythm going on over here But over on this side, this P wave decided to show up early It didn't wait its turn It came early, and it's kind of getting all in the T0516 · Practice EKG Strips (class 6) 01 Identify the following rhythm a Sinus arrhythmia b Sinus arrest with a PAC d Sinus tachycardia with a PVC
The textbook name given to this rhythm, even if your patient is "odd", The pacemaker foci for this rhythm, The rate of this sinus rhythm, By definition, the rate of this rhythm0118 · Sinus rhythm refers to the pace of your heart beat that's set by the sinus node, your body's natural pacemaker A normal sinus rhythm means your heart rate is within a normal rangeThe diagnosis for the strip below is most likely (HINT Patient is in AF at the beginning, then is in sinus rhythm at the end of the strip) Select one a Posttachycardia sinus pause (seen in TachyBrady Syndrome) b ECG Lead fell off of the patient c Functional bundle branch block d Sinoatrial Exit block e Complete AV Block




Image Quiz Common Easily Mistaken Ecg Rhythms Clinician S Brief



Lesson V Ecg Rhythm Abnormalities
Interpreting EKG Rhythm Strips Step 3 – P Wave P wave is produced when the left and right atria depolarize First deviation from the isoelectric line Should be rounded and upright P wave is the SA node pacing or firing at regular intervals This pattern is referred to as a sinus rhythmAtrial rhythms originate in the atria rather than in the SA node The P wave will be positive, but its shape can be different than a normal sinus rhythm because the electrical impulse follows a different path to the AV (atrioventricular) node These EKG differences are covered on our atrial rhythms training module as well as in practice strips · An arrhythmia is any abnormal rhythm other than normal sinus rhythm – the baseline rhythm of the heart This can be a benign variant (like sinus arrhythmia), or it could be deadly (like ventricular fibrillation) In order to know how to read an EKG rhythm strip, you need to first be able to understand what normal sinus rhythm (NSR) looks like




Ecg Learning Center Test




Premature Atrial Contractions Boss Rn
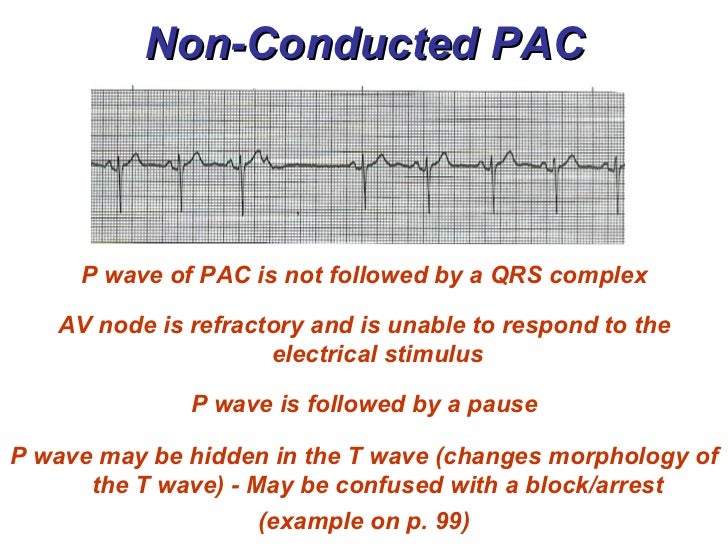
· ECG features of sinus arrhythmia Sinus rhythm with beattobeat variation in the PP interval producing an irregular ventricular rate Sinus rhythm with beattobeat variation in the PP interval producing an irregular ventricular rateThe ECG criteria for premature atrial contractions (PACs) including atrial bigeminy and blocked (nonconducted) PACs are discussed with links to 12lead ECG examples0100 · ECG features of PACs Abnormal (nonsinus) P wave followed by a normal QRS complex (< 1 ms) PACs arising close to the AV node ("low atrial" ectopics) cause retrograde activation of the atria, producing an inverted P wave with a relatively short PR interval ≥ 1 ms (PR interval < 1 ms is classified as a PJC) PACs that reach the SA node may
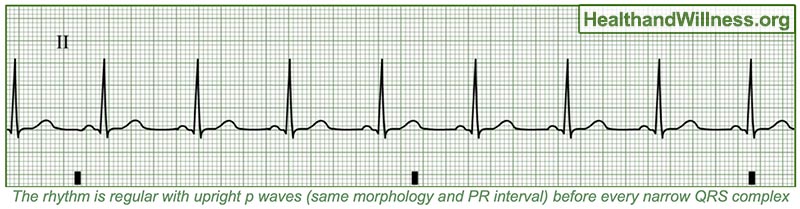



How To Read An Ekg Rhythm Strip Health And Willness




Premature Atrial Contraction Electrocardiogram Wikidoc
Ekg rhythm identification practice by steven jones, nremt–p clemc identify the rhythm • regular or irregular • rate • p wave • pr interval • qrs duration •eptopics / abnormalities sinus bradycardia • regular • 37 • normal • 016 seconds • 008 seconds • none identify the rhythm • regular or irregular • rate • p wave • pr interval • qrs durationEKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus Rhythm Rate 60 100 beats per minute r Rhythrn Atrial Regular Ventricular Regular o Pwaves Uniform in appearance Upright w/ normal shape One Preceding each QRS Nor more than 10 second o PR interval 012 0 second r QRS 010 second or less PWaves Should be no more than 25 mm in height, and no more than 10 second in width · PACs momentarily interrupt the normal sinus rhythm by inserting an extra heartbeat Because a PAC can reset the sinus node, there is usually a short pause before the next normal heartbeat occurs As such, PACs are often perceived as a skip in the heartbeat If you have been told you have PACs, you can rest assured that you are in the majority




Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet




What Doctors Need To Know About Apple Watch Ekg The Hospital Medical Director
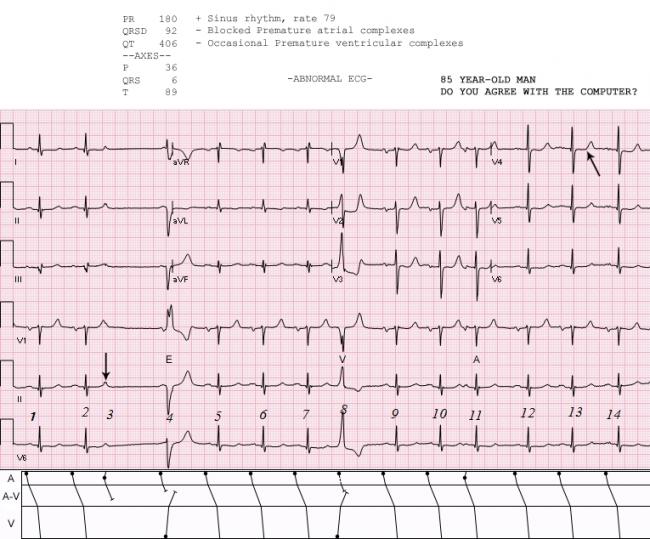
· The rhythm in this tracing (shown in Figure 1 with the ventricular beats/ QRS complexes numbered on the lead II rhythm strip at the bottom) appears to be irregularly irregular If it were regularly irregular, several ECG diagnoses would move up in the differential diagnosis namely, normal sinus rhythm (NSR) with a regular bigeminal, trigeminal, or quadrigeminalRhythm analysis indicates normal sinus rhythm (NSR) at 68 bpm Premature atrial complexes (PACs), Premature junctional complexes (PJCs), and Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are present This encounter shows a normal sinus rhythm with a large amount of ectopy This causes an irregular looking rhythm that can easily confuse beginner monitor techs The presence of PThe ECG strip shows intermittent sinus slowing with two junctional escapes click here to view Junctional Escape Rhythm This is a sequence of 3 or more junctional escapes occurring by default at a rate of 4060 bpm There may be AV dissociation or the atria may be captured retrogradely by the junctional pacemaker In the ECG example below the



1




Premature Atrial Contraction Electrocardiogram Wikidoc
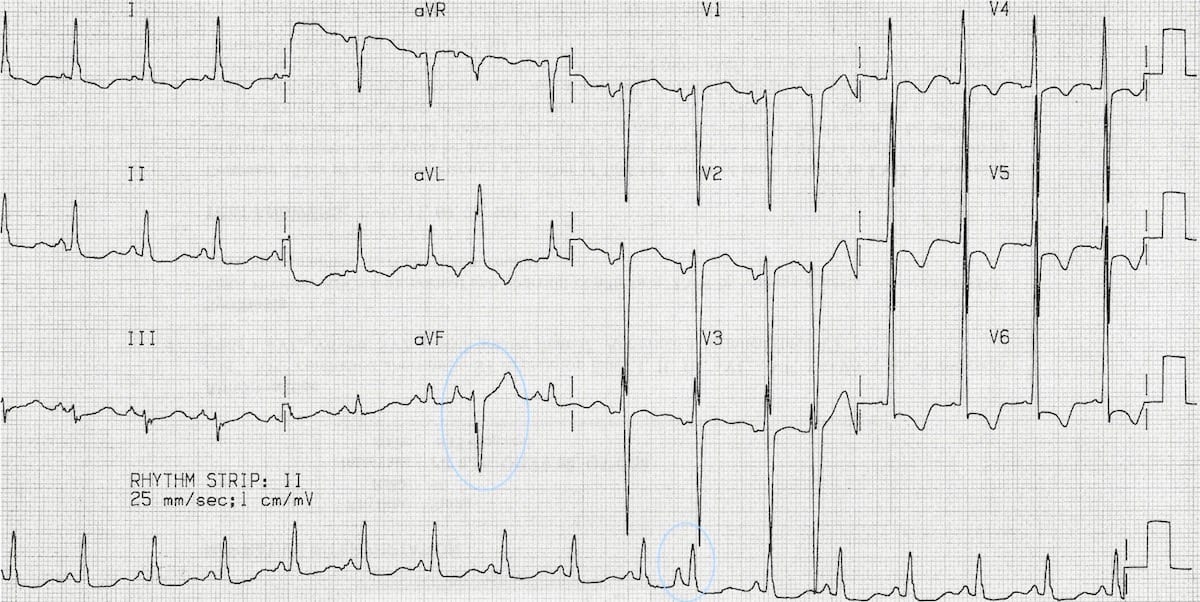
Rhythm Clinical Associations ECG Characteristics Clinical Significance Treatment Strip Sinus Bradycardia Conduction path same as NSR SA node fires at · No notes for slide This slide set contains 46 ECG strips that depict various normal and abnormal cardiac rhythms Sinus Atrial Nodal Heart blocks PACs and PVCs Ventricular SVT Pace competitive rhythms Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia Sinus Arrhythmia Sinus Arrest Premature Atrial ContractionsQuestion 6 In this V1 rhythm strip, what do the 'e' and 'c' represent A The 'e' represents a ventricular echo beat form the nonconducted P wave The 'c' is a sinus capture B The 'e' is for ventricular escape The 'c' is a PAC C The 'e' is a junctional escape, and 'c' represents a PAC
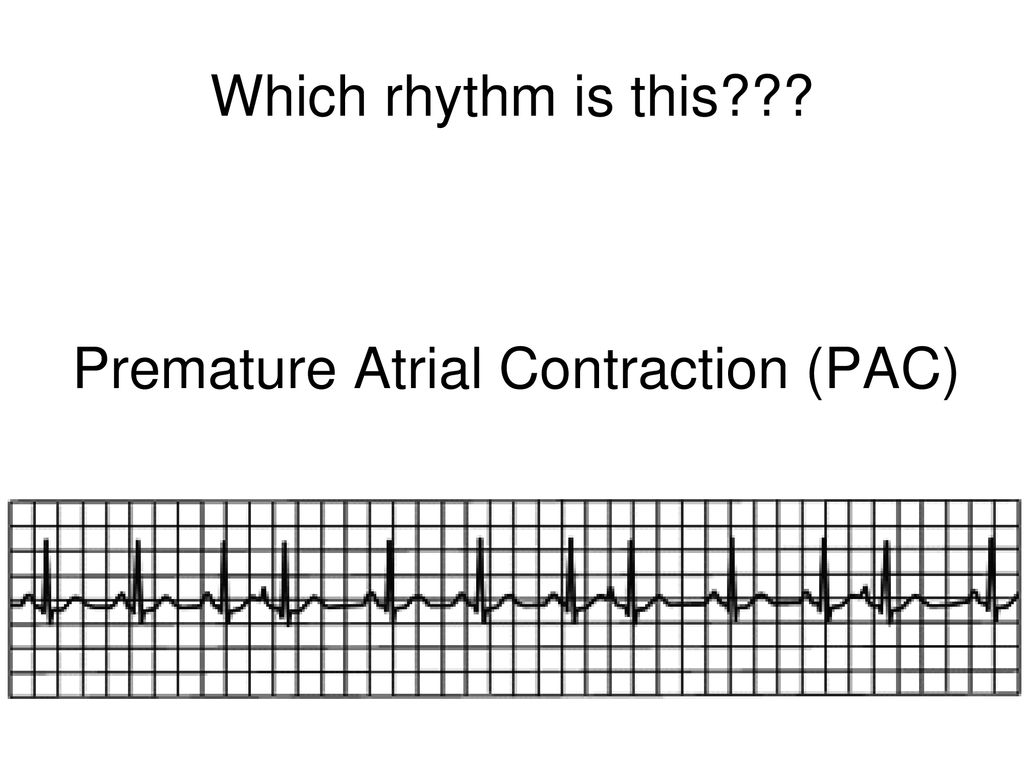



Review Of Ecgs Ppt Download



1
Search for an EKG strip from a simple drop down list Quickly find any rhythm and click go It will pull up a page with an example strip and an easy to understand deicription No lengthy deep learning No digging Just find your strip fast and easy!These junctional escape beats usually occur during a pause in the underlying rhythm (following sinus arrest or block, after premature beats or nonconducted PACs, or during the pause associated with seconddegree AV block Type I) The pause in the rhythm allows a focus in the AV junction to "escape" and pace the heartPremature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are extra, abnormal heartbeats that begin in the ventricles, or lower pumping chambers, and disrupt your regular heart rhythm, sometimes causing you to feel a skipped beat or palpitations PVCs — also called also called premature ventricular complexes, ventricular premature beats and extrasystoles — are very common and usually




Premature Supraventricular Complexes Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography
· The depolarization rate of these pacemaker cells decreases from the sinus node (fastest) to the ventricles (slowest) Ectopic impulses from other pacemaking cells are suppressed by more rapid impulses If an ectopic focus depolarizes prior to the arrival of the next sinus impulse, it may "capture" the ventricles, thereby producing a premature contraction · ECG Interpretation Review 78 (PACs – Atrial Bigeminy – Aberrancy – Blocked PAC – AV Block) The simultaneously recorded 2lead rhythm strip shown below in Figure 1 was obtained from a young adult feeling "skips" Interpreting EKG Rhythm Strips Step 1 – Heart Rate Methods to determine heart rate The 6 second method Denotes a 6 second interval on EKG strip Strip is · So twice, I have come across a situation in which I'll have an EKG strip I'm trying to interpret Some nurses will say it's sinus arrythmia and some say they're just PAC's The rhythm is definitely irregular There seems to be some sort of pattern to it All the complexes (p and QRS) look the same From my understanding, sinus arrhythmia isn't seen very often and it usually increases




Electrocardiography Cardiovascular And Pulmonary Physical Therapy Second Edition An Evidence Based By William E Deturk




Premature Atrial Contraction Pac The Premier Ekg Resource For Medical Professionals Ekg Md Dr Anthony Kashou
· While the sinoatrial node typically regulates the heartbeat during normal sinus rhythm, PACs occur when another region of the atria depolarizes before the sinoatrial node and triggers a premature heartbeat On the EKG, PACs are characterized by an abnormally shaped P waveSinus bradycardia ECG, causes & management Definition of sinus bradycardia Sinus bradycardia fulfills the criteria for sinus rhythm but the heart rate is slower than 50 beats per minute ECG criteria follows Regular rhythm with ventricular rate slower than 50 beats per minute Pwaves with constant morphology preceding every QRS complex Pwave is positiv in limb lead II Normal · ECG recognition of wandering pacer requires a long enough rhythm strip to appreciate gradual change over a period of beats from one P wave morphology to another Technically, there should be at least 3 different atrial sites — in order to distinguish a wandering atrial pacemaker from a simple atrial escape rhythm The clinical reality, is that most of the time




Knowledge Of Ecg N W We Started The Cardiac Dysrhythmias With Ekg Tracings And Methods Of Treatment Management Normal Sinus Rhythm This Is A Normal Heart Rhythm So No Treatment




Pin On Heart Attack
At least three different P wave configurations are seen with this rhythm strip, leading to a claim that this is a multifocal atrial tachycardia Six Second ECG Quiz 2A v21 Annotated Answer Key 5 Question 7 This ECG rhythm is called a) Junctional tachycardia b) Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) c) Sinus tachycardia d) Atrial fibrillation with fast ventricular response Answer bPremature atrial contractions (PACs) are a common cardiac dysrhythmia characterized by premature heartbeats originating in the atria While the SA node (sinoatrial node) typically paces the heart during normal sinus rhythm PACs occur when a region of the atria depolarizes before the SA node can send it's signal, and thus triggers a premature heartbeat The exact cause of PACs is unclear While several predisposing conditions exist, PACs · Normal Sinus Rhythm With PACs Misdiagnosed As Atrial Fibrillation This patient was diagnosed by the rescue crew as having atrial fibrillation, based on the fact that they thought the rhythm was irregular, and they could not see P waves They also noted a wavy baseline, and considered it to be fibrillatory waves




Ekg Atrial Dysrhythmia Atrial Rythms Leveluprn




Ekg Examples Electrocardiography Cardiovascular System
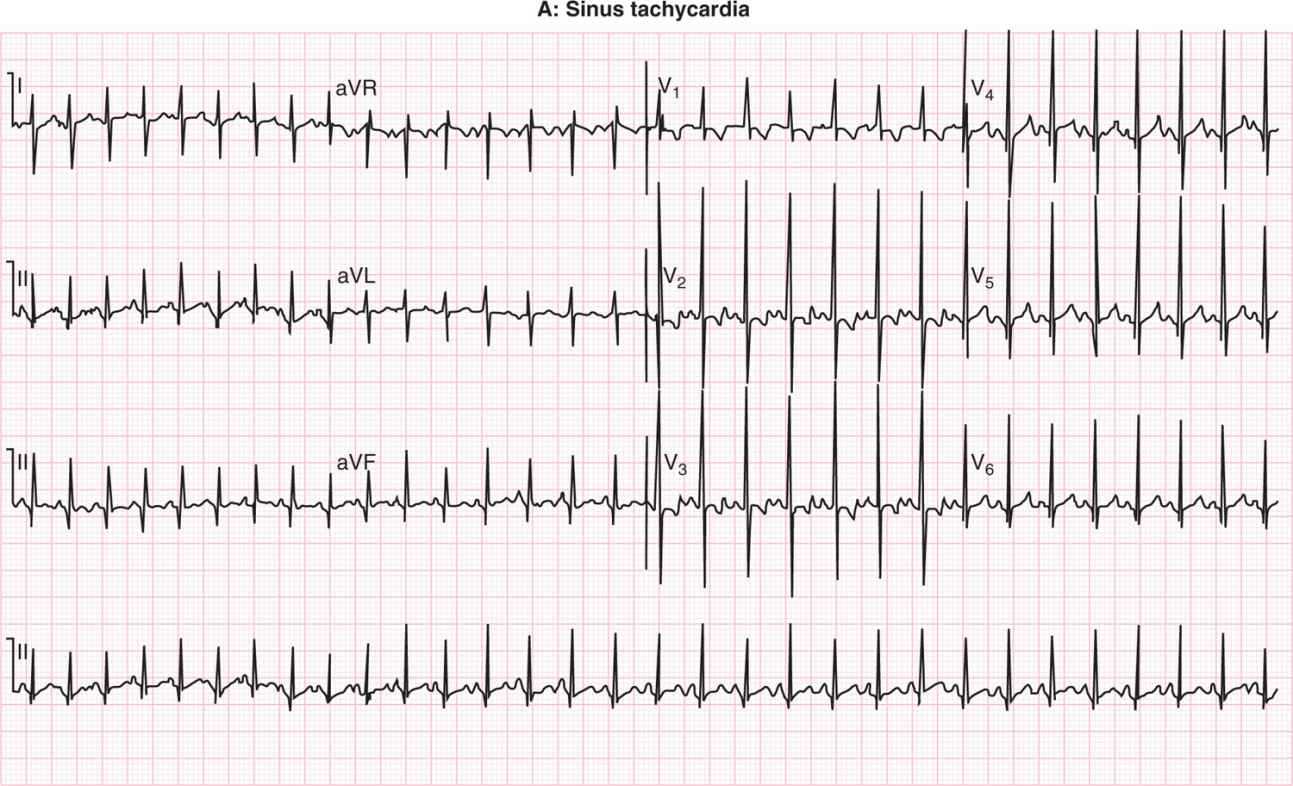
The ECG criteria for sinus tachycardia including causes and treatment are discussed in this review The syndrome of inappropriate sinus tachycardia SIST is mentioned · This Lead II rhythm strip was taken from a 12Lead ECG performed on a 66yearold man who was having an acute inferior wall MI The rhythm is normal sinus rhythm at 65 bpm The QRS complex is slightly wide at 112 ms (11 seconds) The patient did not have a bundle branch block pattern on his 12lead ECG The PR interval is 17 seconds, and the P waves are widenedStart studying EKG strips FINAL Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools




Ecg Interpretation 11
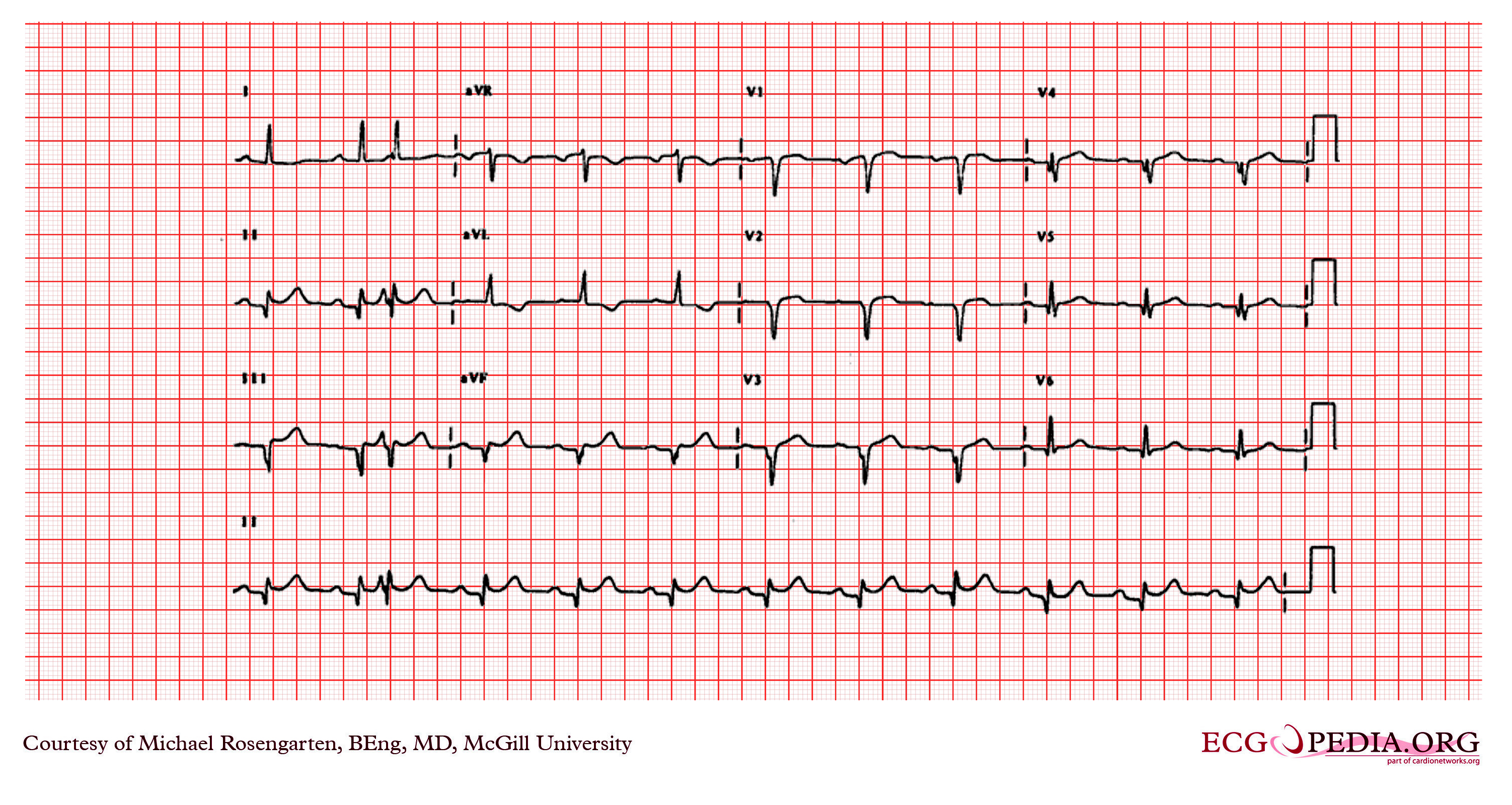



Premature Atrial Contraction Electrocardiogram Wikidoc
Premature atrial contractions, also known as atrial premature complexes or atrial premature beats, are a common cardiac dysrhythmia characterized by premature heartbeats originating in the atria While the sinoatrial node typically regulates the heartbeat during normal sinus rhythm, PACs occur when another region of the atria depolarizes before the sinoatrial node and thus triggers a · View Homework Help EKG stripsdocx from COMPLEX CR NR 341 at Chamberlain College of Nursing SINUS RHYTHM Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia Sinus Arrest SinusEKG Interpretation JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS AND NURSING INTERVENTIONS Objectives ♥Identify specific cardiac dysrhythmias ♥Describe appropriate nursing interventions for specific dysrhythmias Junctional Rhythms Junctional rhythms are named such because their impulse originates from the AV node (AV junction) instead of the SA node The SA node may be impaired



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Paroxysmal Av Block Ems 12 Lead




Premature Atrial Contraction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Type Ii Av Block Ems 12 Lead
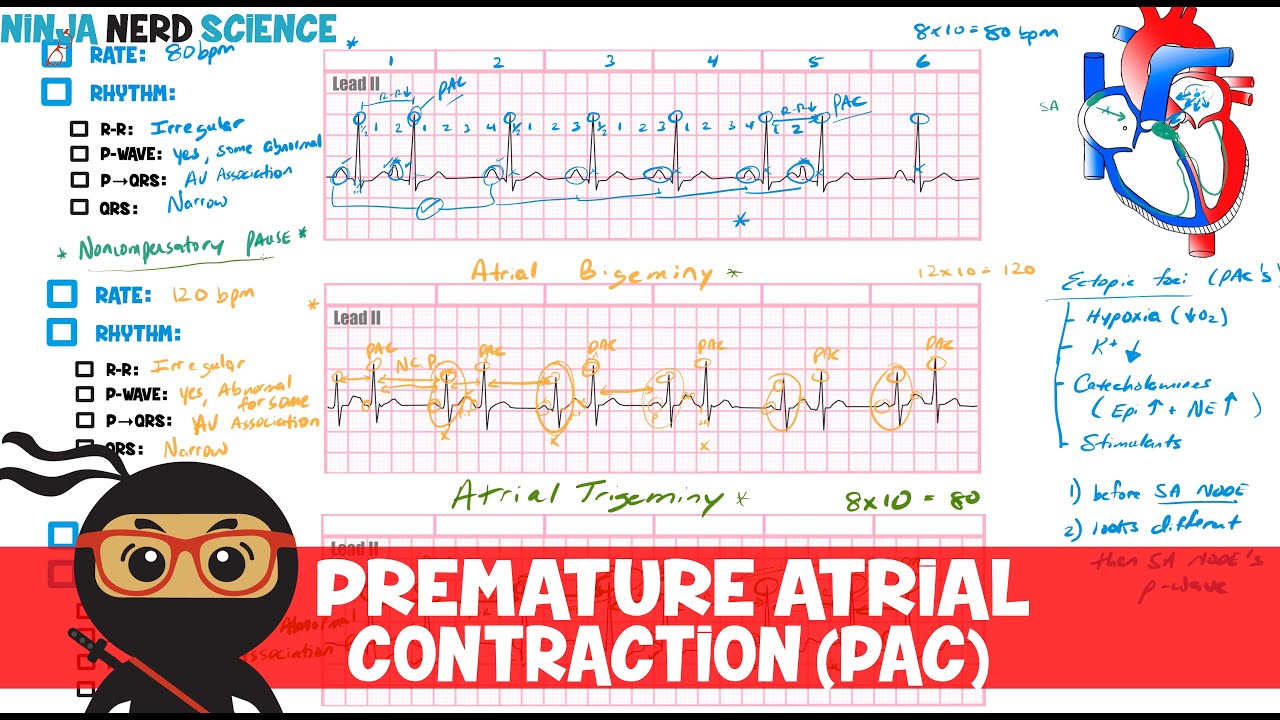



Rate And Rhythm Premature Atrial Contraction Pac Youtube




Http Www Youtube Comwatch V7 Twu 0gklzofeaturerelated Ecg



Nt Prophecyhealth Com Docs Manuals Foundations Of Ecg Interpretation1 Pdf




Ekg Interpretation Cheat Sheet Heart Arrhythmias Guide Update



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Premature Atrial Contractions Are They Benign Or Malignant The Skeptical Cardiologist




Introduction To Telemetry Monitoring For Arrhythmias Nursing Ce Course Nursingce




Telemetry Technician Course Practice Ekg Strips Class 5 Review
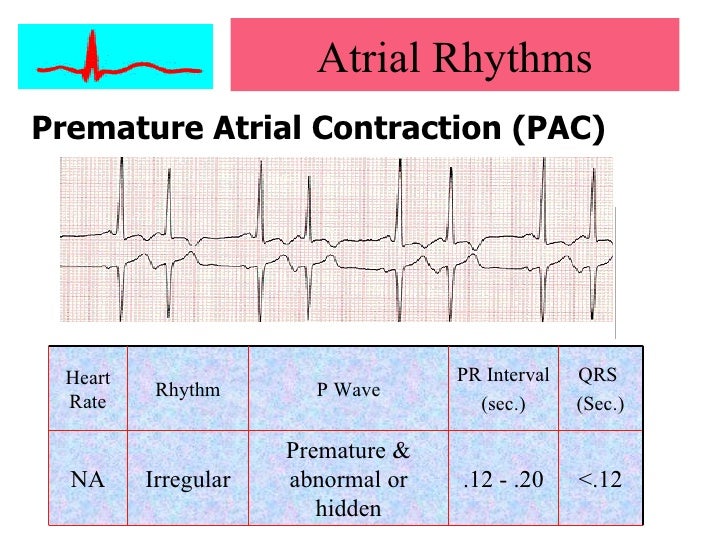



Cardiac Arrhythmias



Sinus Rhythm With Ectopy Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Ekg Ecg Interpretation Course Ceufast Nursing Continuing Education




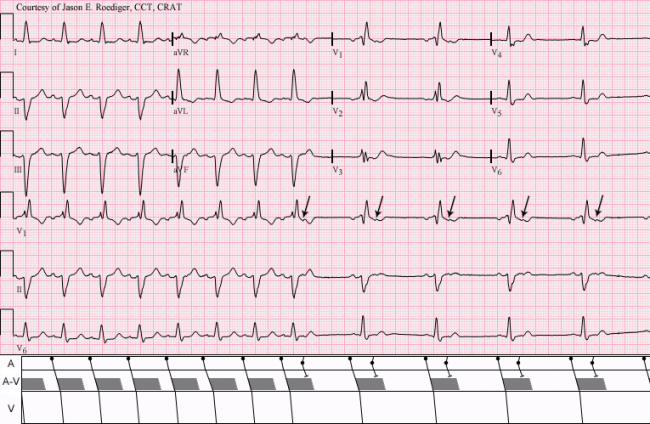
Ecg Review Av Block Or Blocked Pacs 08 09 15 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing
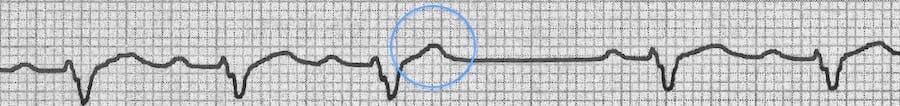



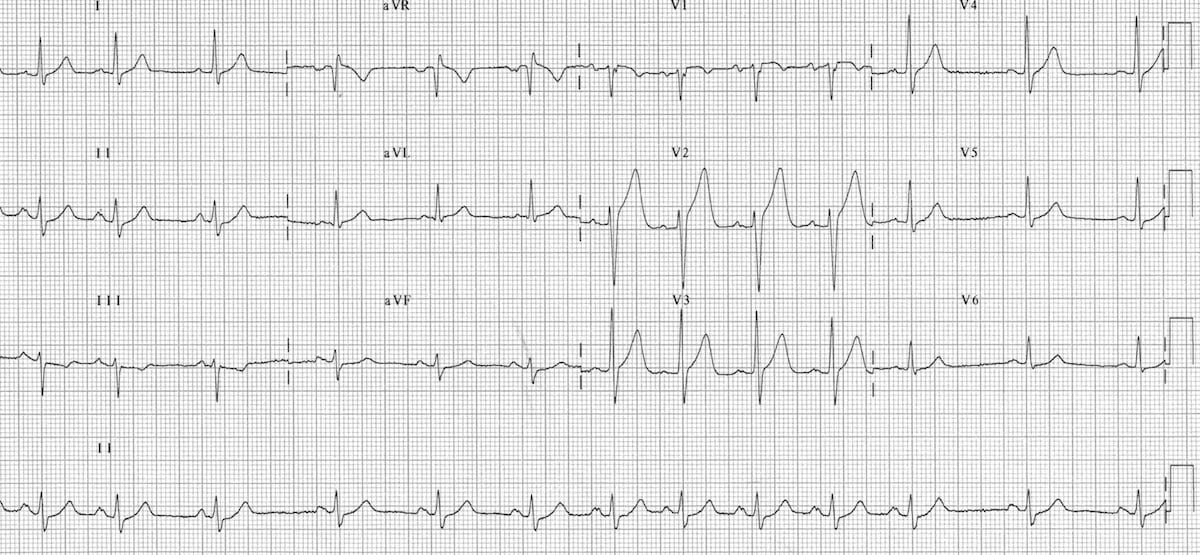
Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Ecg Strips




Premature Atrial Contractions Pacs Animation Youtube




Premature Atrial Contractions Are They Benign Or Malignant The Skeptical Cardiologist




Atrial Rhythms Flashcards Quizlet
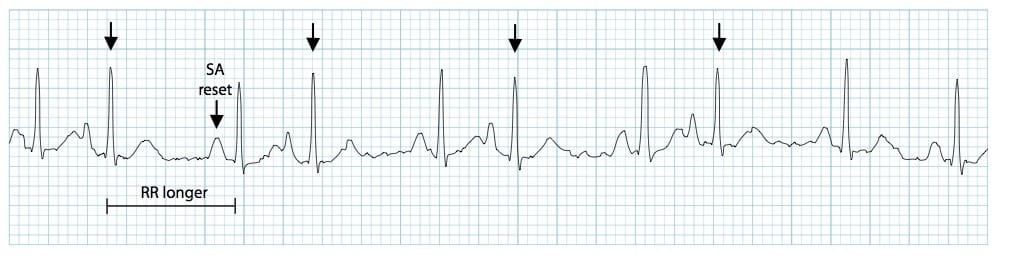



Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Heart Rate And Rhythm Disorders American Academy Of Pediatrics



1
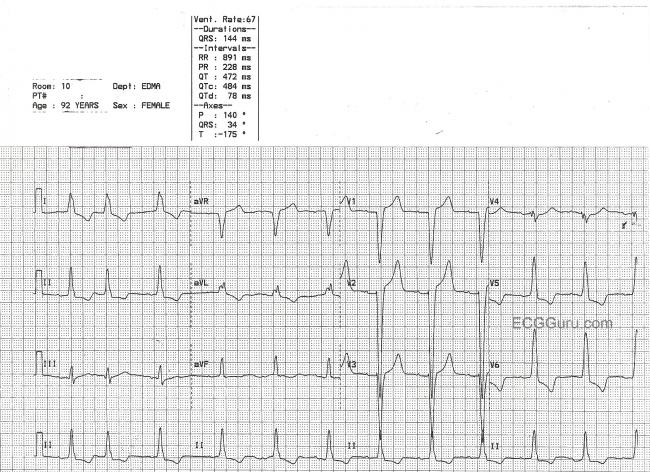



Pac Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Basic Ecg Ekg Interpretation Of Common Arrhythmias




Alivecor Kardia Has A Premature Beat Problem How Pvcs And Pacs Confuse The Mobile Ecg Device The Skeptical Cardiologist




Ecg Interpretation Ecg Blog 155 Arrhythmia Pacs Wandering Mat



Sinus Arrhythmia Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx




Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 78 Pacs Atrial Bigeminy Aberrancy Blocked Pac Av Block



Atrial Rhythms Bmh Tele




Pin On Nurse Life



Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Lesson V Ecg Rhythm Abnormalities




Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Alivecor Kardia Has A Premature Beat Problem How Pvcs And Pacs Confuse The Mobile Ecg Device The Skeptical Cardiologist




Pac Pjc Pvc Pdf 5 Minute Speedy Session Telemetry Pac Pjc Pvc Sinus Rhythm Just A Baseline To Compare To The Other Strips Notice That Every P Wave Has Course Hero




Bigeminy Wikipedia




Ecg Learning Center Test



Premature Atrial Contractions Article




How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography



Ekg Ecg Interpretation Course Ceufast Nursing Continuing Education




Alivecor Kardia Has A Premature Beat Problem How Pvcs And Pacs Confuse The Mobile Ecg Device The Skeptical Cardiologist




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography



Neonatal Arrhythmias Obgyn Key



Premature Atrial Contraction Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Arrhythmias Thoracic Key




Bigeminy Wikipedia



Ekg Strip Search Premature Atrial Contraction Pac



Ecg Of The Month Palpitations And Chest Pain American College Of Cardiology




Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 78 Pacs Atrial Bigeminy Aberrancy Blocked Pac Av Block




Image Quiz Common Easily Mistaken Ecg Rhythms Clinician S Brief




Alternating Bundle Branch Block Circulation



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx




Ecg Interpretation 11




Ecg Learning Center Test



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead



Mark Hammerschmidt Arrythmia Faq



Mark Hammerschmidt Arrythmia Faq




Untitled Document



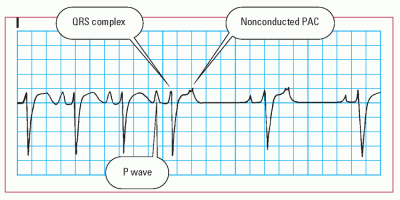
Non Conducted Pacs Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice
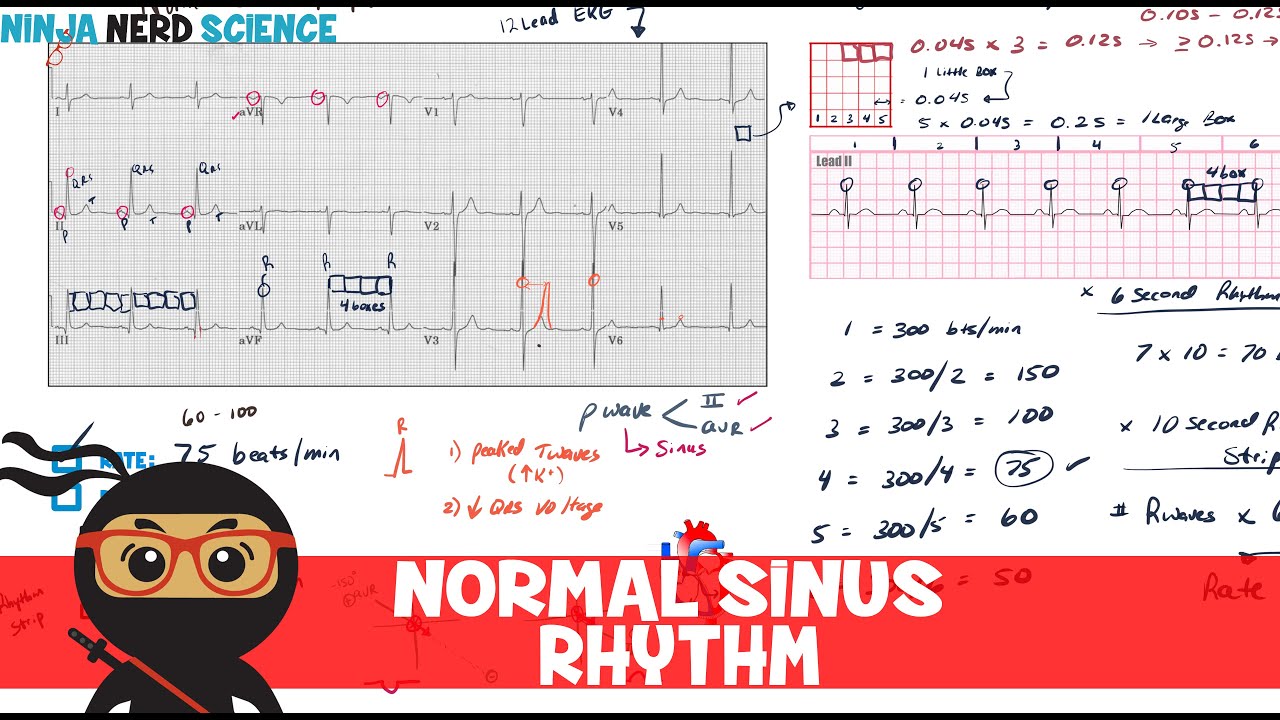



Rate And Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Youtube



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice
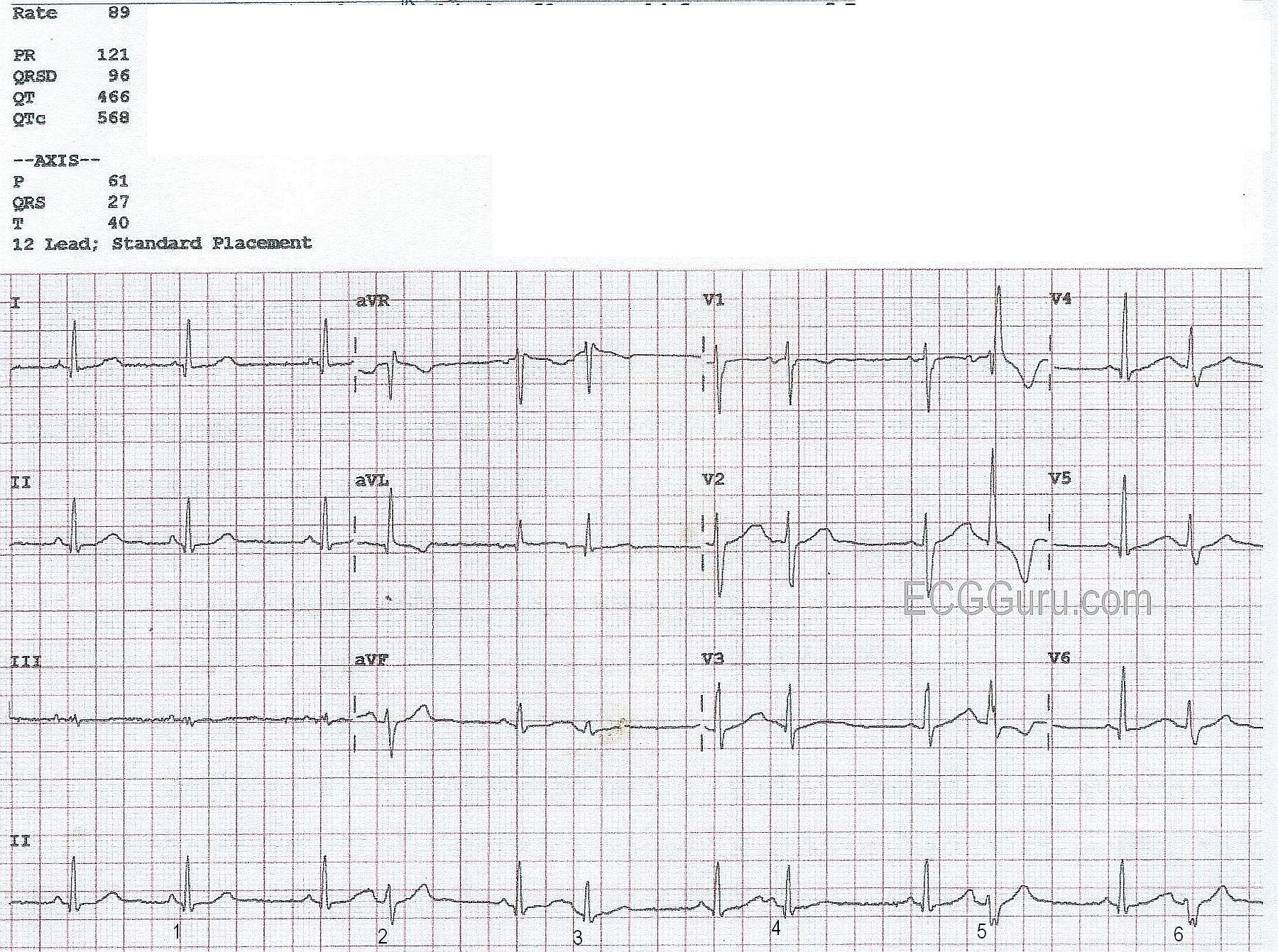



Bigeminal Rhythm With Aberrant Conduction Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Difference Between Premature Atrial Contraction And Atrial Fibrillation Biology Stack Exchange




Basic Ecg Ekg Interpretation Of Common Arrhythmias



Http Www Bremss Org Uploadedfiles File Ekg Intermediate Tips Tricks Tools Pdf




Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Type Ii Av Block Ems 12 Lead
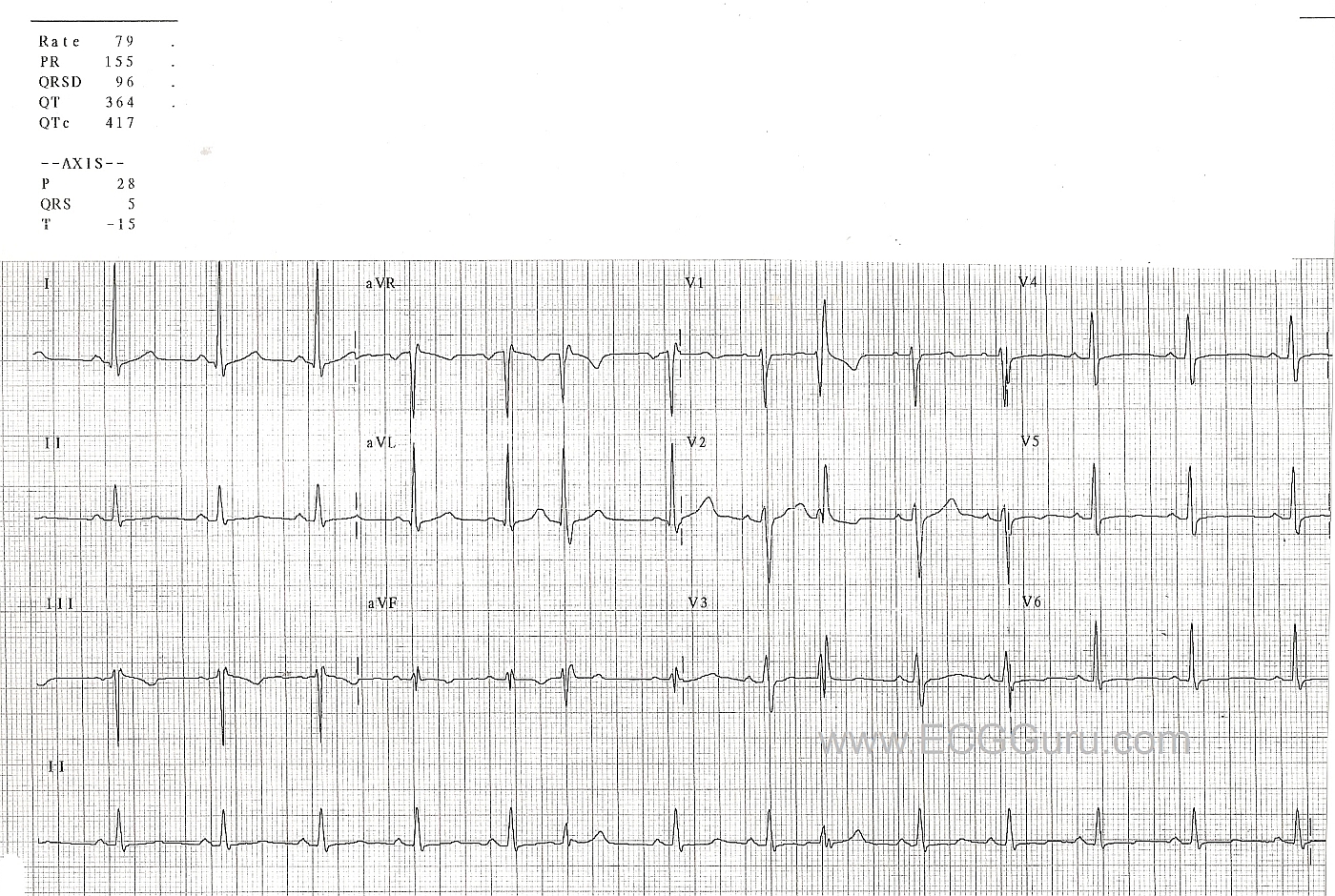



Normal Sinus Rhythm With Aberrantly Conducted Pacs Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Ectopic Complexes And Rhythms Thoracic Key



Med Virginia Edu Emergency Medicine Wp Content Uploads Sites 232 15 10 Introduction To Ecg Rhythms Pdf
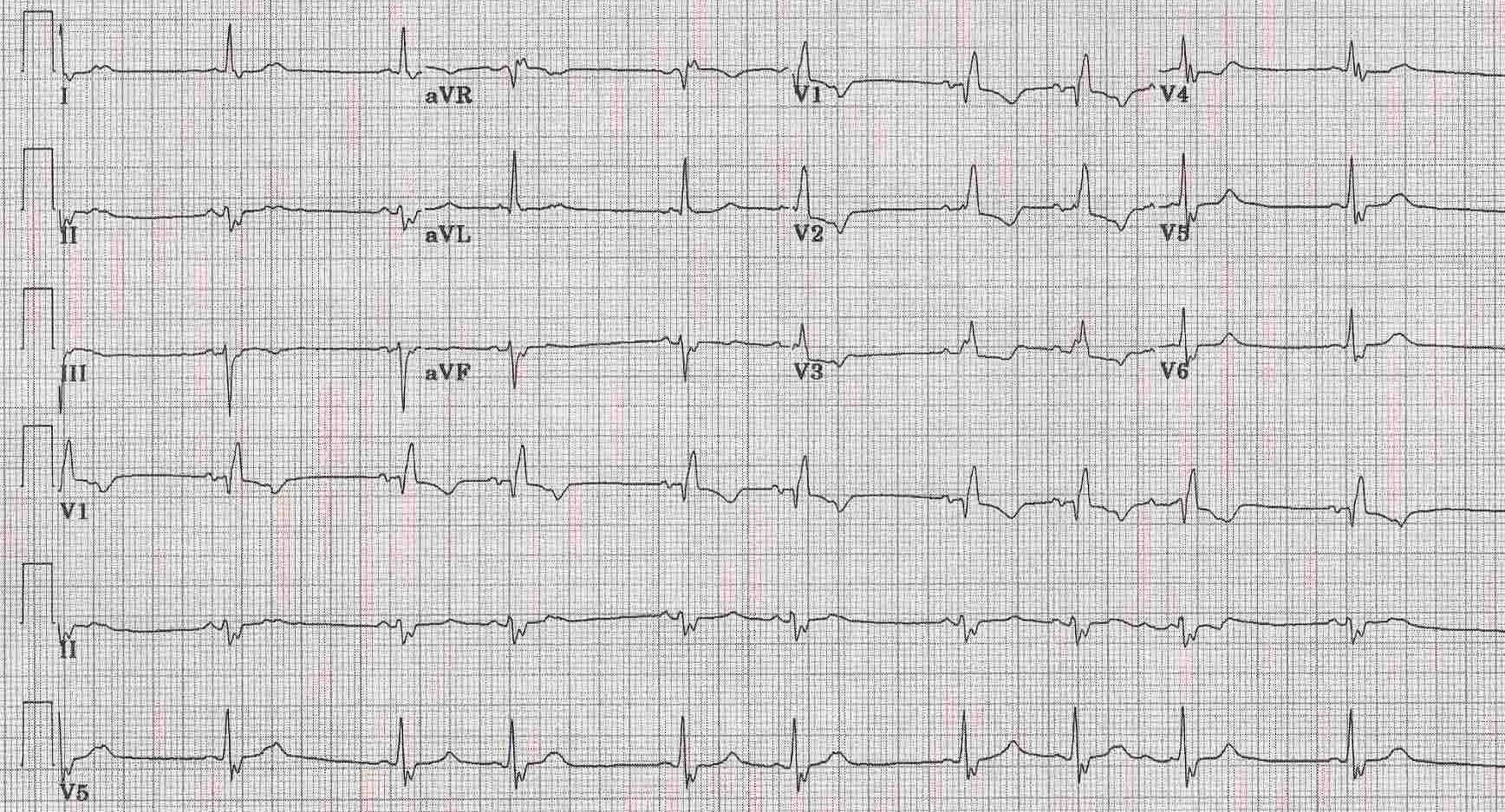



Premature Atrial Contraction Electrocardiogram Wikidoc




Practice Rhythm Strip 1




Sr With Pvc Youtube
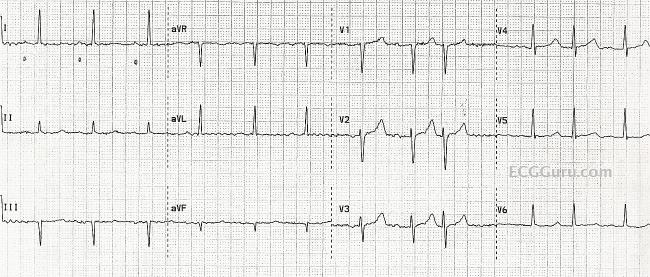



Normal Sinus Rhythm With Pacs Misdiagnosed As Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx



Ekg Strip Search Premature Atrial Contraction Pac



1


コメント
コメントを投稿